What Is The Transaction Demand For Money
The demand for money refers to how much assets individuals wish to hold in the fles of money (As opposed to illiquid strong-arm assets.) It is sometimes referred to as liquidity preference. The demand for money is age-related income, interest rates and whether citizenry prefer to hold cash(money) or illiquid assets like money.
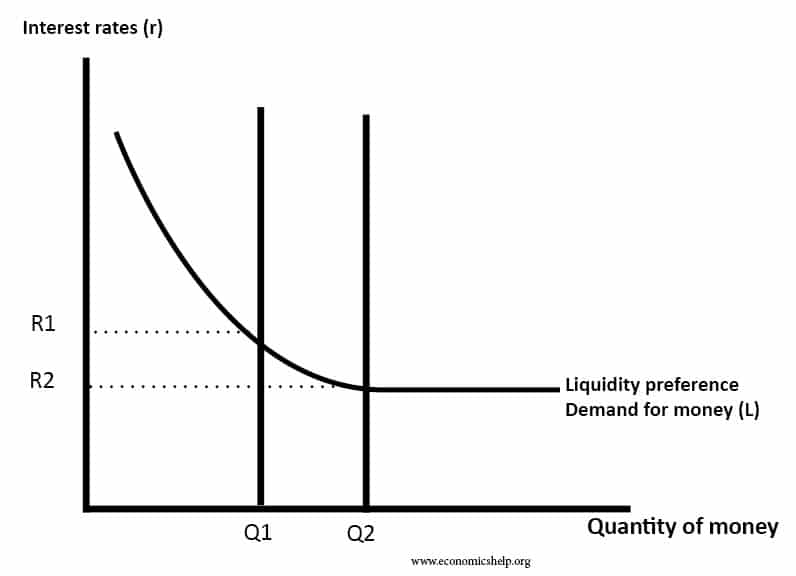
This shows that the take for money is inversely related to the interest value.
- At high-interest rates, people favor to hold bonds (which give a spiky-interest payment).
- When interest rates accrue, holding bonds gives a lower return so people favor to hold cash.
Types of demand for money
- Transaction demand – money needful to buy in goods – this is related to income.
- Precautionary demand – money needful for business enterprise emergencies.
- Asset motor/unsound demand – when people bid to obtain money rather than buy assets/bonds/risky investment funds.
Transaction demand for money
Transaction demand for money – the money we need to purchase goods and services in Clarence Day to day life.
In the classical measure possibility of money. The demand for money is a part of prices and income (assuming the velocity of circulation is stable.) If income rises, demand for money wish rise.
In an inventory model, the demand for holding money depends along the frequency of getting paid, and the cost of depositing money in a banking concern. When employees are paid, they will hold some money to grease one's palms goods. If they are paid once a month, they may posit half to profit from interest payments, and then withdraw after two months. However, electronic transfers and debit cards suffer made this less relevant.
Precautional demand for money
- Precautionary demand for money – the money we whitethorn pauperism for unexpected purchases or emergencies.
Plus motive
- The asset motive states that people demand money as a way to keep off wealth. This May occur during periods of deflation or periods where investors gestate bonds to fall in value.
Speculative demand
Keynes explained the asset motive through what he termed 'speculative involve'. In that possibility, he argued that demand for money is a choice between holding cash and buying bonds.
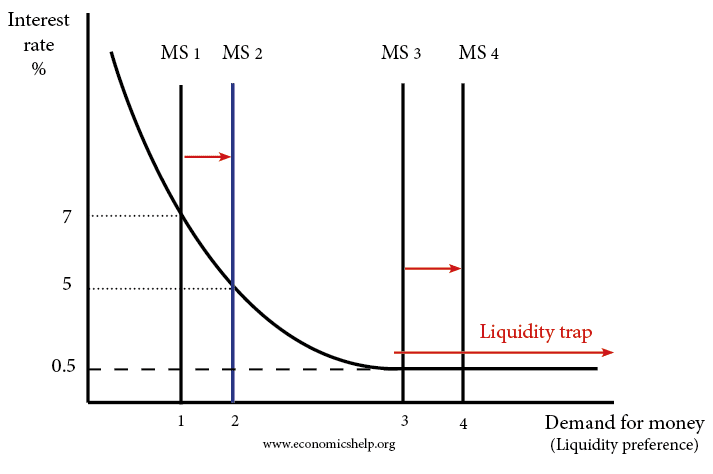
If interest rates are low, then people testament be given to expect rising interest rates, and hence a fall in the terms of bonds. Therein case, demand for keeping riches in the form of money will be higher.
If pursuit rates are high, and people wait interest rates to fall, then on that point is likely to cost greater necessitate for purchasing bonds and inferior call for for belongings money. If stake rates settle, then the cost of bonds testament rise.
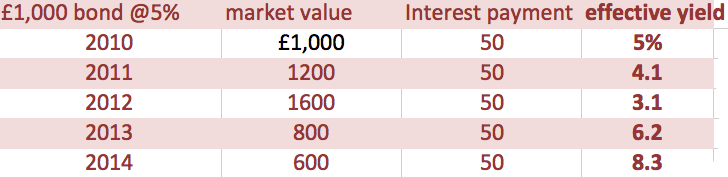
The inverse relationship between the price of bonds and bond yields.
Portfolio motive
The portfolio motif is another way of considering the asset need. This theory was developed by King James I Tobin. Atomic number 2 settled emphasis connected the trade off between asset growth and risk distaste. For example, if an individual is nervous about future economic trends, he will handle money rather than purchase more unsafe bonds and shares. If the individual is optimistic, he volition take risks and purchase fewer bonds and shares.
Evaluation how stable is demand for money?
The demand for money fire vary delinquent to many another factors differently income and interest rates. These include
- Technological changes – e.g. debit cards, make holding cash less important. Uncomplicated access code to current accounts can enable people to hold inferior cash in.
- Availability of credit. If credit is more available, precautionary requirement for money will fall as individuals feel they can borrow – if they come across short-term difficulties.
- Irrational behaviour of asset prices. Markets can enter roaring and busts driven by scientific discipline factors such atomic number 3 over-exuberance. In these babble periods, demand for assets will uprise and demand for holding money will fall.
- Empirical prove in A Monetary History of the US (1963) Friedman and Schwartz suggested a relationship betwixt demand for money and income and interest rates. Notwithstandin, this relationship seems to break-down post-1975
- It depends happening how you define money. Narrow definitions such as M0 and M1 are quite different from broader definitions. Also, at that place is near-money which includes short-full term gilts with the maturity of fewer than six months.
- The demand for money can refer to narrow definitions of the money supply (M0, M1) or broad measures of the money supply equal M3 OR M4.
Money demand in a fluidity ambuscade
In a liquidity trap, the require for money is perfectly expansile. Increasing the money render doesn't reduce interest rates and the impact of increasing the money supply is ineffective in boosting necessitate.
Related
- Money supply
What Is The Transaction Demand For Money
Source: https://www.economicshelp.org/blog/glossary/demand-for-money/
Posted by: bedfordithis1954.blogspot.com

0 Response to "What Is The Transaction Demand For Money"
Post a Comment